Raw Material Analysis
Key words:
Classification:
Key words:
Product Introduction
Bovine Colostrum
BOVINE COLOSTRUM
Bovine colostrum: a native nutritional complex, concentrated essence
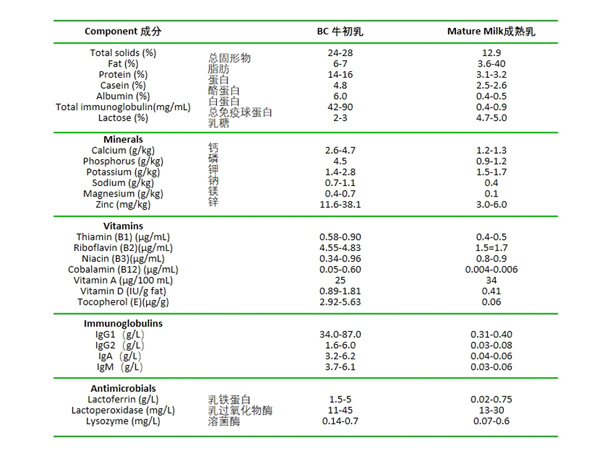
Differences in some functional components and nutrient content between bovine colostrum and mature milk (regular cow's milk). The total protein in bovine colostrum is more than 4 times that of mature milk, and immunoglobulin can be more than 200 times higher, with the most significant difference in IgG content, while IgA is about 50-150 times that of mature milk.
In addition, lactoferrin in bovine colostrum can reach more than 200 times that of mature milk, lactoperoxidase can reach more than 3 times, and lysozyme can reach about 10 times. The differences in minerals and vitamins are not significant; for example, calcium is about 2-4 times, zinc about 2-12 times, vitamin D about 2-4 times, vitamin B2 about 3 times, vitamin B12 more than 8 times, and vitamin E more than 48 times.
Bovine colostrum: a native nutritional complex
Bovine colostrum is an important commercial source of colostrum. Like the well-known superfoods such as turmeric and chia seeds, it is a natural native nutritional complex, and no single component can fully represent it.
Bovine colostrum contains far more than 250 types of native nutrients, including immunoglobulins, antimicrobial peptides, growth factors, cytokines, oligosaccharides, and more. These components play different roles, making bovine colostrum potentially beneficial for immunity, gut health, bones, skin, and more.


N-acetylneuraminic acid
N-acetylneuraminic acid/N-acetylneuraminic acid/bird's nest acid/sialic acid, abbreviated in English as: SA, NANA, Neu5Ac,
CAS No.: 131-48-6, Molecular formula: C11H19NO9, Molecular weight: 309.27. The main sources of N-acetylneuraminic acid in nature are bird's nests, breast milk, etc. In nature, because bird's nests contain a high content of N-acetylneuraminic acid, it is also a standard for judging the classification and grade of bird's nests. Bird's nest is a traditional high-grade tonic, and when we mention bird's nest, we think of beauty, longevity, and the efficacy of bird's nest comes from N-acetylneuraminic acid. When we talk about bird's nest, we are actually referring to bird's nest acid.
On May 31, 2017, the National Health and Family Planning Commission included SA in the new food raw material directory. Our company became the third domestic enterprise to obtain production license approval for N-acetylneuraminic acid in April 2020. The product can be applied in: maternal and infant formula, dietary supplements, functional foods, antiviral drugs, and cosmetics.
Product Consulting
Filling in your phone and E-mail information will help us to get in touch with you in time and solve your problems as soon as possible.
Contact Us
Contact Phone:
Address: Shenyang East Street, Limin Development Zone, Harbin City, Heilongjiang Province, Changsha Road South




